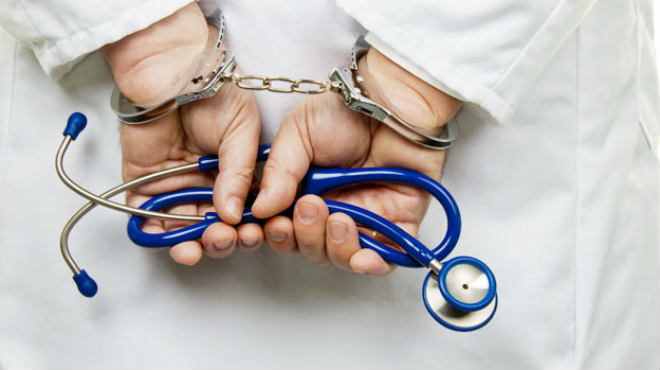
Medical negligence, often termed as medical malpractice, is a serious concern globally, including in India. The implications of medical negligence can be profound, leading to physical, emotional, and financial distress for patients and their families. In India, where the healthcare system is undergoing rapid evolution, addressing medical negligence is crucial to ensure the trust and well-being of patients. This article aims to elucidate the concept of medical negligence within the Indian legal framework, its implications, and the available remedies.
Legal Framework:
In India, medical negligence falls under the purview of civil law, primarily governed by the Indian Contract Act, 1872, the Consumer Protection Act, 2019, and various judgments passed by Indian courts. Under these laws, medical professionals owe a duty of care to their patients, which includes providing treatment with reasonable skill and diligence. Failure to meet this standard amounts to negligence.
Elements of Medical Negligence:
To establish medical negligence, certain elements must be proven:
1. Duty of Care: The medical professional must owe a duty of care to the patient. This duty arises when a doctor-patient relationship is established.
2. Breach of Duty: There must be a breach of the duty of care, i.e., the medical professional fails to provide treatment in accordance with the accepted medical standard. This breach is often assessed by comparing the doctor’s actions with what a reasonable medical practitioner would have done in similar circumstances.
3. Causation: The breach of duty must directly cause harm to the patient. It must be demonstrated that the negligent act or omission was the proximate cause of the injury or adverse outcome.
4. Damages: Finally, the patient must suffer actual harm or damages as a result of the negligence. These damages can include physical injury, emotional trauma, financial loss, or loss of earning capacity.
Implications of Medical Negligence:
Medical negligence can have severe consequences for patients, including:
1. Physical Harm: Negligent medical treatment can exacerbate existing health conditions or lead to new injuries, illnesses, or disabilities.
2. Emotional Distress: Patients and their families often endure significant emotional distress due to the physical and psychological impact of medical negligence.
3. Financial Burden: Medical negligence can result in additional medical expenses, loss of income due to inability to work, and expenses related to ongoing care and rehabilitation.
4. Loss of Trust: Instances of medical negligence erode public trust in the healthcare system and can have far-reaching implications for doctor-patient relationships.
Remedies Available:
In India, patients have several avenues to seek redress for medical negligence:
1. Civil Lawsuits: Patients can file civil lawsuits against the negligent medical professional or institution to claim compensation for damages suffered. These lawsuits are typically filed in the appropriate civil court and may involve the assessment of expert medical opinion.
2. Consumer Protection Act: The Consumer Protection Act, 2019, provides a forum for consumers to seek compensation for deficient services, including medical services. The District Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission, State Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission, and National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission handle such cases.
3. Medical Council Proceedings: Patients can file complaints against erring doctors with the respective State Medical Council or the Medical Council of India. These councils have the authority to investigate allegations of medical negligence and take disciplinary action against the concerned medical professionals, including suspension or revocation of their medical licenses.
4. Criminal Proceedings: In cases of gross medical negligence leading to death or grievous harm, patients or their families may initiate criminal proceedings against the negligent medical professionals under sections 304A (causing death by negligence) or 338 (causing grievous hurt by act endangering life or personal safety of others) of the Indian Penal Code.
Conclusion:
Medical negligence is a serious issue in India with far-reaching consequences for patients and the healthcare system. It is imperative for medical professionals to uphold the highest standards of care and for patients to be aware of their rights and avenues for seeking redress in cases of negligence. By fostering accountability and transparency within the healthcare system, we can mitigate the incidence of medical negligence and ensure the well-being of patients across the country.

They handle all the insurance paperwork seamlessly.
where to buy generic lisinopril without rx
Unrivaled in the sphere of international pharmacy.
They set the tone for international pharmaceutical excellence.
where to buy generic clomid no prescription
Their international insights have benefited me greatly.
Always ahead of the curve with global healthcare trends.
where buy cheap cipro without rx
Their 24/7 support line is super helpful.
The drive-thru option is a lifesaver.
can i purchase cheap clomid for sale
Their global reach is unmatched.
I’m grateful for their around-the-clock service.
mixing gabapentin and soma
A pharmacy that takes pride in community service.
Their adherence to safety protocols is commendable.
where can i buy cytotec price
I’m always informed about potential medication interactions.